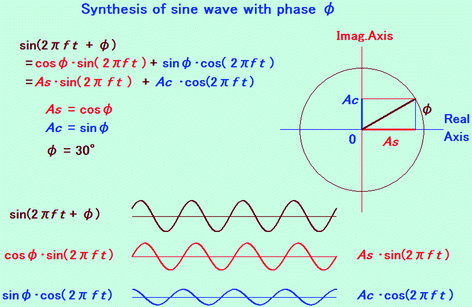
How does the term sin (2*pi*f*t) come from? I know that sin and cosine take radians as arguments which will be (pi/2) * (no. of degrees) but why do we mulitply f*t?

SOLVED: Using separation of variables method to solve the IBVP Utt = Uxx; 0 <x<1 t>0 u(o,t)=0=u(1,t) u(x, 0) = 2 sin (Tx) 4(x, 0) = sin (2tx) produces the general solution
How does the term sin (2*pi*f*t) come from? I know that sin and cosine take radians as arguments which will be (pi/2) * (no. of degrees) but why do we mulitply f*t?

A transverse wave is described by the equation y = y0sin2pi ( ft - xt ) . The maximum velocity of the particle is equal to four times the wave velocity, if

A transverse wave is described by the equation y = y0sin2pi ( ft - xt ) . The maximum velocity of the particle is equal to four times the wave velocity, if

χ and χ ⋅ ⟨sin(2π f t) sin(2π f t + φ)⟩o as a function of f obtained... | Download Scientific Diagram

Using numerical analysis of ordinary differential equation systems to predict the chemical concentration after plasma irradiation: AIP Advances: Vol 12, No 5





![The set of values of x in [ 0,2π] for which fx=√sin x+cos x is defined is The set of values of x in [ 0,2π] for which fx=√sin x+cos x is defined is](https://df0b18phdhzpx.cloudfront.net/ckeditor_assets/pictures/1418755/original_sinx.png)